The Impact of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence has become a must have skill and critical basis for strong leadership.
Daniel Goleman, who popularized EI, describes emotional intelligence (EI) as a different way of being smart and cites it as a critical factor underpinning high performance and exceptional leadership.
“It’s not your IQ; it’s how you manage yourself and your relationships.” – Daniel Goleman
Being an emotionally intelligent leader can pay dividends when it comes to inspiring teams, managing stress, staying focused, delivering feedback, empathizing with colleagues, and working together toward a shared goal.
And the benefits don’t stop there.
If you’ve ever wondered about the impact emotional intelligence can have on personal and professional development, consider these findings:
- Studies show 90% of top performers have high emotional intelligence and a higher average annual income
- Empathic leaders perform more than 40% higher in employee engagement, coaching, and decision-making
- More than 95% of surveyed founders stated EQ (emotional intelligence) in leadership is more important than IQ
- People with high levels of emotional intelligence earn an average of $29,000 more a year
Developing EI happens one person at a time — it starts with you and me — but our growth can be felt by the people in our life. Friends, family, and colleagues are all impacted when we practice emotional intelligence.
As a predictor of life success, EI has become one of the most highly valued and sought after skill sets, with no slowdown in sight. By 2024, global demand for EI skills is actually expected to increase by 6x.
The good news is the economic value and business case for EI has been well made.
Even better news? Emotional intelligence is both teachable and learnable.

If you’re ready to jumpstart your emotional intelligence journey, you can learn the 12 emotional intelligence (EI) competencies from Daniel Goleman’s EI model through a series of facilitated, six-week online courses: Foundational Skills and Relational Skills.
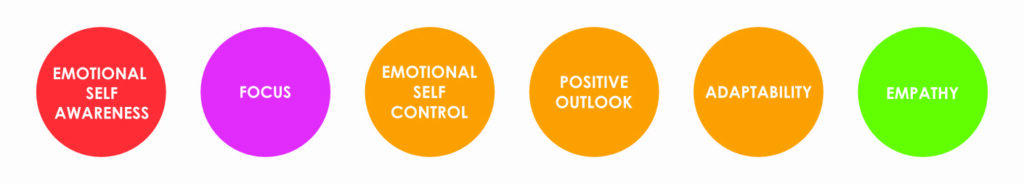
The EI skills included in the Foundational Skills Course: Emotional Self-Awareness, Focus, Emotional Self-Control, Positive Outlook, Adaptability, and Empathy.
The EI skills included in the Relational Skills Course: Conflict Management, Teamwork, Inspirational Leadership, Coach and Mentor, Influence, and Organizational Awareness.

These 12 competencies are crucial for developing your best self, becoming an outstanding leader, and building high-performance teams.
As part of an engaged cohort and led by a trained facilitator, you can join a community of peers and experts while learning the science behind each core competency, why they matter, and how to apply them to positively differentiate yourself, build deeper relationships, and pave a path toward fundamental transformation.
Grow your EI and earn a certified digital achievement badge while:
- Developing one of the most in-demand and highly valued job skills
- Mastering the underlying abilities that make stellar leaders
- Achieving greater self-awareness, self-worth, and values alignment
- Building positive relationships and meaningful connections
Invest in emotional intelligence today. Your future self will thank you.
Learn more about upcoming courses at courses.keystepmedia.com.















