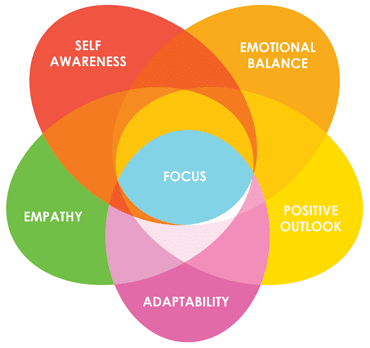
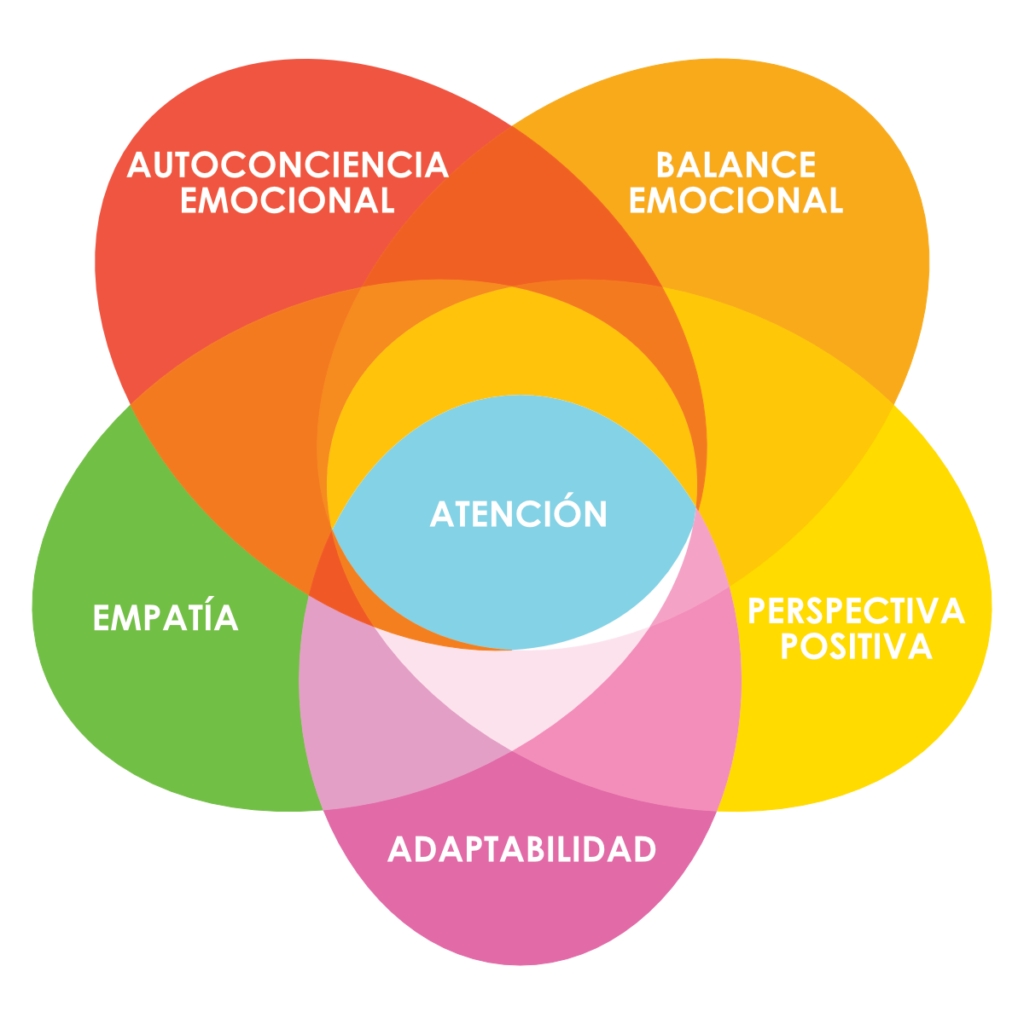
Scientists tell us the adaptive ability of any system is usually gauged by its response to disruptions or challenges. In the case of the human system, a.k.a. you and me, adaptive abilities mean you are a person who is flexible in handling change, juggling multiple demands, and navigating new situations with innovative ideas and approaches.
Is This Me?
Think about these statements, and choose A or B:
- A) I tend to think of change as bad. B) I tend to see change as an opportunity.
- A) I dislike change. B) Some change can be worthwhile.
- A) I feel uptight when plans change at home or work. B) I find changes in plans energizing.
- A) I hate making adjustments in my routines. B) I make adjustments to routines easily.
- A) I feel threatened when a challenge arises. B) I like a challenge.
- A) I often get “locked in” to an idea or approach to solving a problem. B) I’m open to new information when solving a problem.
If you find yourself agreeing with most of the A statements, you may be someone who is uncomfortable with change. If you find yourself agreeing with more of the B statements, you may be more able to adapt as changes demand.
Looking at your own beliefs and judgments can be an important first step toward greater adaptability. If you are fixed in your thinking, you may struggle against change rather than turning it into an opportunity. Learning to sit with discomfort amidst uncertainty is something every human can benefit from.
An agile mindset is one that recognizes that adapting to change is the price of admission for living a meaningful life. Let’s face it, any time you try something new, you face uncertainty and there is risk involved. You never know exactly how things will turn out. For example, you may have to make a decision about whether to take a new job or stay where you are. There are no guarantees the job will be a good fit. If it is, great! You took the leap and it paid off. If the new job isn’t great–you chalk it up to learning. You are wiser, you gain new skills, new connections, and you’re able to translate that into a better decision next time. The bottom line: change is difficult, uncomfortable, and at times downright painful. Our ability to effectively handle the discomfort of change improves through experimentation and repetition.
Here’s how rigidity, the opposite of adaptability, can show up at work: Imagine an executive who quickly shuts down an idea suggested by a team member for a more tech-based system of project management that could increase productivity. The executive may not realize this “shut-down” reflex has become an unconscious habit, triggered by any suggestion of change, which results in his automatically coming up with reasons the new idea won’t work, rather than why it might. Such a habit keeps things as they are and squelches innovation. This lack of adaptability keeps inefficient practices in place, and, maybe worse, sends a message not to question the status quo. Over time, this results in stagnation, reduced passion, and energy and weaker financial results.
However, imagine if that executive had been more adaptable and asked the rest of the team how they feel about the new idea and whether it’s worth trying. If they express enthusiasm, the adaptable executive might give it a chance to see how it goes. If it works, progress is made. If it doesn’t, something useful could still be learned. There is acknowledgement that innovation and change carry emotional and financial outlays. And the emotional outlay can be lessened with an emotionally agile mindset.
Adaptability is at the heart of innovation in any environment.
People who demonstrate adaptability combine curiosity and problem solving skills to achieve their goals. Persistence leads them to try new behaviors or methods of getting things done. They are resourceful and creative, especially when budgets are tight. These key building blocks to adaptability–agility, persistence, and trying multiple strategies–are vital skills for success.
Increasingly, adaptability is a key differentiator of effective leadership in highly tumultuous industries, such as technology and finance. Leaders who show strong adaptability recognize that their industry is continually changing and are better able to evolve. They realize they can’t be stuck doing the same old thing over and over. They think creatively and take calculated risks.
There are numerous case studies of once-thriving companies whose leaders were unable to embrace change, such as Blockbuster, Sears, and Kodak. Alternatively, we all know companies that make phenomenal examples of adaptability, including Apple and Google, who created new products we didn’t even know we needed. They were attuned to shifting trends and feedback from customers.
Consider current workplace norms: teams are no longer fixed and steady, they form and disassemble; work is increasingly meted out in short-term contracts. And leaders are attempting to prepare a workforce for jobs that don’t yet exist. It should not be surprising then that employers are putting a high priority on the skill of adaptability.
By staying adaptable and open-minded, you continue to reinvent yourself and experience significant growth along the way.
Keep in mind, there are times when there’s a good reason not to change, like preserving quality standards or time-tested effective strategies. The trademark of an adaptable leader, however, is the ability to balance core values with responsiveness in the face of a changing world.
Try this exercise for developing your adaptability
Think of a change in either your personal or professional life you have recently experienced or are currently experiencing. How do you feel about the change? How are you responding to the change?
Here are some examples of situations that require adaptability:
We are launching a new service line. I’m excited about the possibilities it creates, but a little nervous about whether we’ve thought of everything. I’m doing significant research to position myself as an expert.
My daughter just turned 12 and is suddenly becoming moody and withdrawn, spending lots of time in her room and not talking to me or her Dad. I’m scared something might be going on that she’s not telling us.
Now, ask yourself a series of questions to help find a positive perspective on that change:
- What opportunities does this change represent?
- What positive outcome could I find in this change?
- What is outside of my control?
- What is within my control?
- What is the next (small) action I can take to move in a positive direction?
- What is the best outcome that might result?
Avoiding change is impossible. Instead we can change our relationship to change. We can learn to turn toward what scares us, and in turn, we gradually adapt and grow amidst uncertainty and discomfort in life.